How Skillate is facilitating Inclusiveness in Recruitment with AI
50% of all hiring is a failure.
Sounds impossible, isn’t it? In a process involving experts with years of know-how of recruiting, as well as hiring managers and interviewers with decades of industry experience, it is unthinkable that the success rate of hiring decisions is not more than the probability of heads in a coin toss!

Why does it happen, though? Why do years of experience and knowledge result in such mixed results?
The answer lies in the single biggest problem in recruitment - ‘Bias.’
Human decisions are inherently biased. And with time, the biases only become more concrete. Whether it is attraction towards similar personality, affection towards particular institutes, confirmation bias, halo effect, or ignorance or hatred towards a specific community, all these biases tend to come at work when it comes to hiring.
Hiring biases not only keeps the best candidates away, resulting in more failures; but it also can severely damage the employer branding of organizations. Recently, American Express invested $1 billion to advance racial and gender equality to promote social justice among the masses.
Understanding the importance of the subject, Skillate has introduced AI into the recruitment process, aiming to minimize biases by removing human interventions. This is how the process works:
Masking PII:
Skillate system ensures that any Personally Identifiable Information (PII) like name, email, photo, gender, religion, ethnicity is masked to ensure that there is no bias because of the given information.

- Skill similarity and culture:
Skillate’s AI understands the skills required from the JD, and also has the knowledge of the ‘cluster’ associated or similar to a particular skill. For ex:
If a recruiter is looking to hire a data scientist in the field of ML, he or she might get confused with software developers who mention ML simply after doing a two-month virtual course.
The Skillate system on the other hands understands the ecosystem around ML as a technology and would prefer candidates who have worked on Computer Vision, NLP, Deep Learning, Neural Network, CNN, RNN or used TensorFlow/ Keras etc. This differentiation in terms of the level of skill helps recruiters immensely.
The Skillate AI refrains from using the notorious “Past Hiring Pattern Analysis” that is known for aggravating hiring biases in the past.
- Title Relevancy:
A practical problem that most recruiters face is searching candidates by job titles. While some functions have clearly defined job titles, most new-age positions are named in a multitude of ways. For example: while searching for a sales role - any of the following job titles will be a good fit - Sales Manager, BD Manager, Zonal Manager, or Assistant Manager Sales.
The Skillate AI has the knowledge of different job titles that can refer to the same position. This ensures that a quality candidate is not missed out even if his or her position is named differently.
- Data Normalization:
Traditional keyword matching often searches for exact terminologies in resumes , meaning if you are looking for someone who has worked in AWS, you might miss out on someone whose experience is of working in Amazon Web Services!
Skillate’s vast library of 120 Million profiles tells the system about the various formats and abbreviations of a particular term, meaning you never miss out on quality candidates whatever terminology they use!

- Contextual understanding:
Consider the following two statements:
'Currently working as a Data Scientist at <Amazon>’ and,
‘Worked in a project for the client Amazon ’
In the first statement, “Amazon” will be tagged as a company as the statement is about working in the organization.
But the latter “Amazon” should be considered as a normal word and not as a company. It is evident that the same word can have different meanings, based on its usage.
Skillate AI understands the context behind terms used in the resume , and treats them separately as - simple phrases or specific names as intended. Here is how the technology works:
Now consider one more example, with two statements:
‘2000–2008: Professor at Harvard’
‘B.Tech in Computer Science from Harvard’
This is how Skillate AI processes it:

Here, Harvard is treated as an Employer Organisation in the former statement and as an Educational Institution in the later. We can differentiate between the two meanings of ‘Harvard’ here by observing the context. The first statement has ‘Professor’ which is a Job Title, indicating that Harvard be treated as a Professional Organisation. The second one has a degree and major mentioned, which point towards Harvard being tagged as an Educational Organisation.
Skillate applies a deep learning model Named Entity Recognition (NER) for information extraction in resumes.
- Industry Relevance:
Recruiters often like to hire parallely from industries similar to their organization’s. The Skillate system recognizes this requirement and ranks profiles from similar experience and backgrounds higher than the others.
For example: If a recruiter is looking to hire a salesperson for an FMCG company. The search results will rank a sales profile from Mondelez higher than that from Accenture.
- Removing educational biases:
An often complained bias, specially from candidates is that companies have too much focus on the pedigree of the institution and not enough on the relevant skills or experience. Not only does the Skillate system takes into account a combination of skill, experience and education to rank a profile; but it also has the knowledge of the particular courses relevant to specific institutes.
For ex; if a recruiter is searching for an engineering talent - a graduate from MIT will be a preference. However, if he is looking for an MBA talent - the profile from Stanford would rank higher.
- Measuring Diversity:
One of the most overlooked processes while assessing diversity in recruitment is a procedure to measure its different elements.
Skillate reveals your current hiring trends based on gender, ethnicity, age, geography, etc. to highlight any existing biases in the current recruiting system.
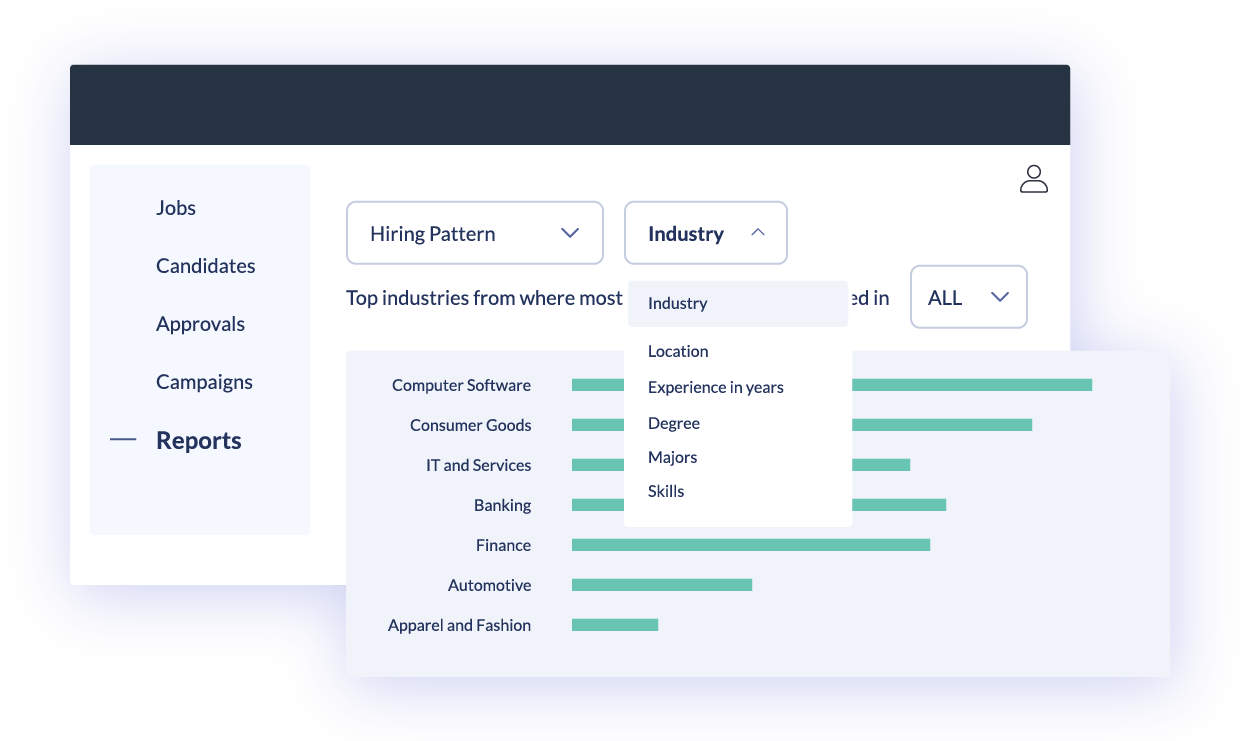
Skillate has been at the forefront of using AI to eliminate human biases by automating recrutement. Other global examples like Microsoft using its SEEING AI and ORBIT (Object Recognition for Blind Image Training) to facilitate inclusivity for the disabled and Gartner predicting a three fold rise in the number of specially- abled hires by 2023 due to AI and emerging technologies only strengthens our vision to remove recruiting biases via AI.
AI in recruitment has evolved over the years. After its initial limitations, it is now not only empowering inclusion in organizations but is also amping up the hiring success rate in the process.
Use it so that your next hire has more probability of being successful than a toss of the coin!
References:
Analytics India| Business Insider